QLogic QLE2562 dual port 8Gb Fibre Channel host bus adapter card. QLogic Corporation was an American manufacturer of networking server and storage networking connectivity and application acceleration products, based in Aliso Viejo, California through 2016.
- Qlogic Scsi & Raid Devices Drivers
- Qlogic Scsi & Raid Devices Driver Win 7
- Qlogic Scsi & Raid Devices Driver Download
- Download and Drivers for Qlogic NetXtreme II 10Gb Driver for Windows.
- The Marvell QLogic QLE2690 single-port and QLE2692 dual-port Enhanced 16Gb FC (16GFC) HBAs boast industry-leading native FC performance with extremely low CPU usage and full hardware offloads. Enhanced 16GFC Compared to 16GFC, the Marvell QLogic Enhanced 16GFC solution offers higher per-port performance (up to 650K IOPS) with low power consumption.
- The following resources are provided as a courtesy to our users. The products represented are no longer supported by QLogic Technical Services.
- Marvell QLogic Enhanced 16GFC Adapters, powered by StorFusion technology, include advanced capabilities that are enabled when deployed with supported Brocade® and Cisco® switches. By combining these industry-leading solutions, SAN administrators can take advantage of enhanced features that improve availability, accelerate deployment.
The Linux SCSI Target Wiki
Fibre Channel fabric module(s) | |
| Original author(s) | Nicholas Bellinger Andrew Vasquez Madhu Iyengar |
|---|---|
| Developer(s) | Datera, Inc. |
| Initial release | July 21, 2012 |
| Stable release | 4.1.0 / June 20, 2012; 8 years ago |
| Preview release | 4.2.0-rc5 / June 28, 2012; 8 years ago |
| Development status | Production |
| Written in | C |
| Operating system | Linux |
| Type | Fabric module |
| License | GNU General Public License |
| Website | datera.io |
- See LIO for a complete overview over all fabric modules.
Fibre Channel (FC) provides drivers for various FC Host Bus Adapters (HBAs). Fibre Channel is a gigabit-speed network technology primarily used for storage networking.
Contents
|
Overview
Fibre Channel is standardized in the T11 Technical Committee of the Inter National Committee for Information Technology Standards (INCITS), an American National Standards Institute (ANSI) - accredited standards committee.
Fibre Channel has been the standard connection type for storage area networks (SAN) in enterprise storage. Despite its name, Fibre Channel signaling can run on both twisted pair copper wire and fiber-optic cables.
The Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP) is a transport protocol which predominantly transports SCSI commands over Fibre Channel networks.
Hardware support
The following QLogic Fiber Channel HBAs are supported in 4/8-gigabit mode:
- QLogic 2400 Series (QLx246x), 4GFC
- QLogic 2500 Series (QLE256x), 8GFC (fully qual'd)
The QLogic Fibre Channel fabric module (qla2xxx.ko, Linux kernel driver database) for the Linux SCSITarget was released with Linux kernel 3.5 on July 21, 2012.[1]
With Linux 3.9, the following 16-gigabit QLogic Fibre Channel HBA is supported, which makes LIO the first open source target to support 16GFC:
- QLogic 2600 Series (QLE266x), 16GFC, SR-IOV
With Linux 3.9, the following QLogic CNAs are also supported:
- QLogic 8300 Series (QLE834x), 16GFS/10 GbE, PCIe Gen3 SR-IOV
- QLogic 8100 Series (QLE81xx), 8GFC/10 GbE, PCIe Gen2
Enable target mode
By default, the upstream qla2xxx driver runs in initiator mode. To use it with LIO, first enable Fibre Channel target mode with the corresponding qlini_mode module parameter.[2]
To enable target mode, add the following parameter to the qla2xxx module configuration file:
Depending on your distribution, the module configuration file might be different, for instance:
- /etc/modprobe.d/qla2xxx.conf: CentOS, Debian, Fedora, RHEL, Scientific Linux
- /etc/modprobe.conf.local: openSUSE, SLES
In order for these changes to take effect, the initrd/initramfs will need to be rebuilt.
Please verify that initrd/initramfs is accepting the additional qla2xxx parameter.
targetcli
targetcli from Datera, Inc. is used to configure Fibre Channel targets. targetcli aggregates LIO service modules via a core library, and exports them through an API, to provide a unified single-node SAN configuration shell, independently of the underlying fabric(s).
Cheat sheet
| Command | Comment |
|---|---|
| /backstores/iblock create my_disk /dev/sdb | Create the LUN my_disk on the block device /dev/sdb |
| /qla2xxx create <WWPN> | Create a Fibre Channel target |
| In /qla2xxx/<WWPN>: luns/ create /backstores/iblock/my_disk | Export the LUN my_disk |
| In /qla2xxx/<WWPN>: acls/ create <Initiator WWPN> | Allow access for the initiator at <WWPN> |
| /saveconfig | Commit the configuration |
Startup
targetcli is invoked by running targetcli as root from the command prompt of the underlying LIO shell.
Upon targetcli initialization, the underlying RTSlib loads the installed fabric modules, and creates the corresponding ConfigFS mount points (at /sys/kernel/config/target/<fabric>), as specified by the associated spec files (located in /var/target/fabric/fabric.spec).
Display the object tree
Use ls to list the object hierarchy, which is initially empty:
Per default, auto_cd_after_create is set to true, which automatically enters an object context (or working directory) after its creation. The examples here are modeled after this behavior.
Optionally, set auto_cd_after_create=false to prevent targetcli from automatically entering new object contexts after their creation:
Create a backstore
Create a backstore using the IBLOCK or FILEIO type devices.
For instance, enter the top-level backstore context and create an IBLOCK backstore from a /dev/sdb block device:
targetcli automatically creates a WWN serial ID for the backstore device and then changes the working context to it.
The resulting object hierarchy looks as follows (displayed from the root object):
Alternatively, any LVM logical volume can be used as a backstore, please refer to the LIO Admin Manual on how to create them properly.
For instance, create an IBLOCK backstore on a logical volume (under /dev/<volume_group_name>/<logical_volume_name>):
Again, targetcli automatically creates a WWN serial ID for the backstore devices and then changes the working context to it.
Instantiate a target
The Fibre Channel ports that are available on the storage array are presented in the WWN context with the following WWNPs, for instance:
- 21:00:00:24:ff:31:4c:48
- 21:00:00:24:ff:31:4c:49
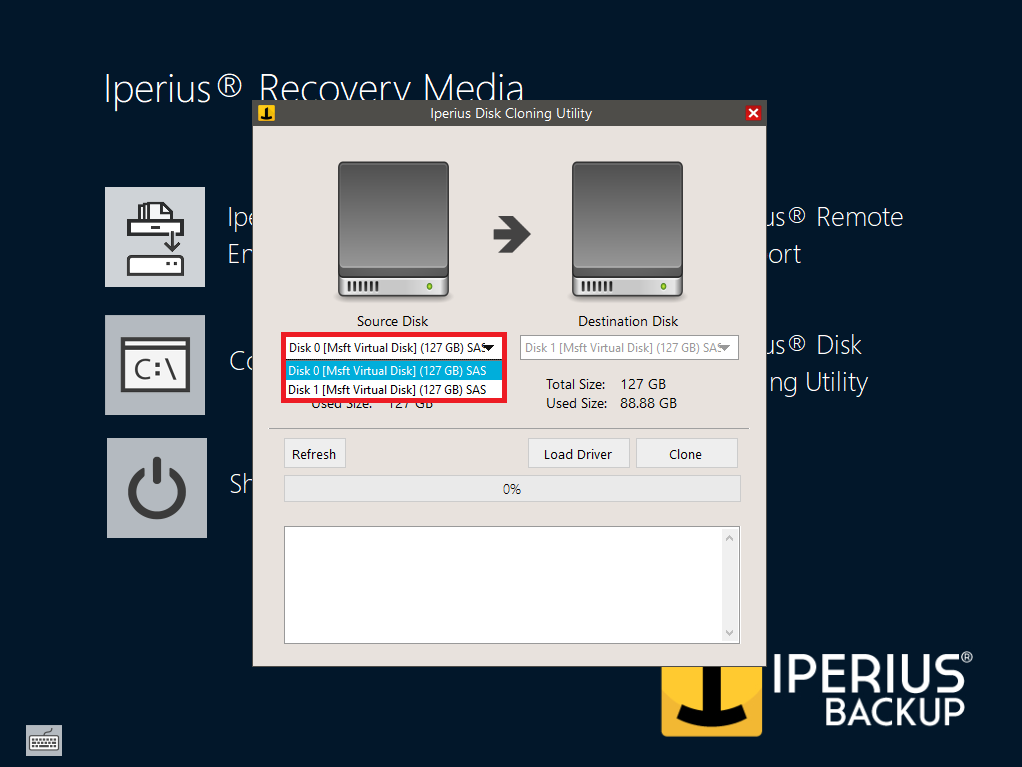
Instantiate a Fibre Channel target, in this example for QLogic HBAs, on the existing IBLOCK backstore device my_disk (as set up in targetcli):
targetcli automatically changes the working context to the resulting tagged Endpoint.
Export LUNs
Declare LUNs for the backstore device, to form a valid SAN storage object:
targetcli per default automatically assigns the default ID '0' to the LUN, and then changes the working context to the new SAN storage object. The target is now created, and exports /dev/sdb as LUN 0.
Return to the underlying Endpoint as the working context, as no attributes need to be set or modified for standard LUNs:
Define access rights
Qlogic Scsi & Raid Devices Drivers
Configure the access rights to allow logins from initiators. This requires setting up individual access rights for each initiator, based on its WWPN.
Determine the WWPN for the respective Fibre Channel initiator. For instance, for Linux initiator systems, use:
For a simple setup, grant access to the initiator with the WWPN as determined above:

targetcli per default automatically adds the appropriate mapped LUNs.

Display the object tree
The resulting Fibre Channel SAN object hierarchy looks as follows (displayed from the root object):
Persist the configuration
Use saveconfig from the root context to persist the target configuration across OS reboots:
Spec file
Datera spec files define the fabric-dependent feature set, capabilities and available target ports of the specific underlying fabric.
In particular, the QLogic spec file /var/target/fabric/qla2xxx.spec is included via RTSlib. WWN values are extracted via /sys/class/fc_host/host*/port_name in wwn_from_files_filter, and are presented in the targetcliWWN working context to register individual Fibre Channel port GUIDs.
Scripting with RTSlib
Setup script
The following Python code illustrates how to setup a basic Fibre Channel target and export a mappedLUN:
Note that while Fibre Channel TPGs are masked by targetcli, they are not masked by RTSlib.
Qlogic Scsi & Raid Devices Driver Win 7

Object tree
The resulting object tree looks as follows:
Specifications
The following specifications are available as T10 Working Drafts:
- Fibre Channel Protocol (FCP): FCP defines the protocol to be used to transport SCSI commands over the T11 Fibre Channel interface, 1995-12-04
- SCSI Fibre Channel Protocol - 2 (FCP-2): FCP-2 defines the second generation Fibre Channel Protocol to be used to transport SCSI commands over the T11 Fibre Channel interface, 2002-10-23
- Fibre Channel Protocol - 3 (FCP-3): FCP-3 defines the third generation Fibre Channel Protocol to be used to transport SCSI commands over the T11 Fibre Channel interface, 2005-09-13
- Fibre Channel Protocol - 4 (FCP-4): FCP-4 defines the fouth generation Fibre Channel Protocol to be used to transport SCSI commands over the T11 Fibre Channel interface, 2010-11-09
Glossary
- Host Bus Adapter (HBA): provides the mechanism to connect Fibre Channel devices to processors and memory.
RFCs
- RFC 2625: IP and ARP over Fibre Channel
- RFC 2837: Definitions of Managed Objects for the Fabric Element in Fibre Channel Standard
- RFC 3723: Securing Block Storage Protocols over IP
- RFC 4044: Fibre Channel Management MIB
- RFC 4625: Fibre Channel Routing Information MIB
- RFC 4626: MIB for Fibre Channel's Fabric Shortest Path First (FSPF) Protocol
See also
- LinuxIO, targetcli
- FCoE, iSCSI, iSER, SRP, tcm_loop, vHost
Notes
- ↑Linus Torvalds (2012-07-21). 'Linux 3.5 released'. marc.info.
- ↑Nicholas Bellinger (2012-09-05). 'Re: targetcli qla2xxx create fails'. spinics.net.
External links
- RTSlib Reference Guide [HTML][PDF]
- Fibre Channel Wikipedia entry
- QLogic Wikipedia entry
- QLogic website
- Emulex website
- T11 home page
| Timeline of the LinuxIO | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Release | Details | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | ||
| 4.x | Version | 4.0 | 4.1 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Feature | LIO Core | Loop back | FCoE | iSCSI | Perf | SRP | CM WQ | FC USB 1394 | vHost | Perf | Misc | 16 GFC | iSER | Misc | VAAI | Misc | DIF Core NPIV | DIF iSER | DIFFC vhost | TCMU Xen | Misc | Misc | virtio 1.0 | Misc | NVMe OF | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Linux | 2.6.38 | 2.6.39 | 3.0 | 3.1 | 3.2 | 3.3 | 3.4 | 3.5 | 3.6 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 3.9 | 3.10 | 3.11 | 3.12 | 3.13 | 3.14 | 3.15 | 3.16 | 3.17 | 3.18 | 3.19 | 3.20 | 3.21 | 3.22 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Qlogic Scsi & Raid Devices Driver Download
